23 Leading Quantum Computing Companies Worldwide [2025 List]
2025.03.20 · Blog
Quantum computing stands at the frontier of technological innovation, promising exponential leaps in processing power and solving problems that traditional computers cannot tackle.
As this field rapidly evolves, many quantum computing companies are leading the charge in quantum research, driving innovations in both quantum hardware and software development.
In this article, we explore a curated list of leading quantum computing companies, offering insights into their unique quantum systems and contributions to the field.
#1 IBM
IBM has long been a trailblazer in the quantum computing field, consistently pushing the envelope of both quantum hardware and software innovations. With decades of research and development, IBM's quantum initiatives are at the forefront of the industry, empowering researchers and enterprises worldwide to explore quantum phenomena and develop novel algorithms.
IBM's approach leverages superconducting qubit technology, backed by extensive research in error correction and quantum algorithms. The company has built a robust ecosystem, including IBM Quantum System, advanced quantum processors, cloud access through the IBM Quantum Platform and a thriving developer community centered around the open-source Qiskit framework.
IBM Key Achievements on Quantum Hardware
Superconducting Qubits: IBM has developed advanced superconducting qubit systems, including the 127-qubit Eagle processor, 433-qubit Osprey quantum processor, 1,121-Qubit Condor quantum processor, Heron R2 Processor. These developments have set industry benchmarks for improving qubit coherence times and connectivity, and reducing error rates.
Scalable Quantum Systems: IBM has pioneered scalable quantum hardware with IBM Quantum System One and IBM Quantum System Two. IBM's commitment to scalable quantum architectures paves the way for fault-tolerant quantum computing.
IBM Key Achievements on Quantum Software
Cloud-Based Quantum Computing: By providing cloud access via the IBM Quantum Platform (previously known as IBM Quantum Experience), IBM democratizes quantum computing. This platform gives users worldwide the opportunity to run experiments on real quantum hardware, bridging the gap between theoretical research and practical application.
Qiskit Framework: IBM's Qiskit is a comprehensive, open-source, end-to-end platform that allows researchers and developers to design, simulate, and execute quantum circuits. Qiskit not only serves as an educational tool but also powers a wide array of research applications in quantum chemistry, optimization, and beyond.
IBM's Quantum Roadmap
By 2025, IBM plans to unveil its first quantum-centric supercomputer, integrating modular processors, middleware, and quantum communication. Their goal is to exceed 4,000 qubits by interconnecting multiple processor chips in the same computer, a critical step toward large-scale quantum machines.
By 2026, IBM aims to enhance quantum circuits with up to 7,500 gates, automating quantum circuits and improving computational depth. This will enable more complex quantum operations and expand practical applications.
By 2033, they plan to have quantum-centric supercomputers that will include thousands of logical qubits capable of running 1 billion gates, unlocking the full power of quantum computing.
#2 Google
Google Quantum AI is committed to developing a practical, large-scale quantum computer that utilizes superconducting qubits. Their work encompasses both quantum hardware and software, employing a full-stack approach that includes the development of quantum processors and user-friendly quantum software solutions. Their mission is to explore how quantum computing can advance machine learning and solve complex computational problems.
Google Key Achievements on Quantum Hardware
Over the years, Google has developed several quantum processors, each building upon the last, to push the boundaries of what quantum computers can achieve.
Google's Sycamore Processor
Sycamore, a 54 qubits (but only 53 were functional during the experiment) superconducting qubit-based quantum processor, gained significant attention in 2019 when it demonstrated quantum supremacy by solving a problem in 200 seconds that would take the world's fastest supercomputer approximately 10,000 years.
Google's Willow Chip
Willow, featuring 105 superconducting qubits, is a more recent development in Google's quantum computing hardware. Willow chip can perform complex computations in under five minutes, a task that would take today's fastest supercomputers an unfathomable 10 septillion years. This processor effectively reduces errors exponentially as more qubits are added, achieving a breakthrough in quantum error correction.
Google Key Achievements on Quantum Software
The Cirq framework, Google's open-source quantum programming library, supports the design, simulation, and execution of quantum circuits on both simulated and real hardware.
#3 SpinQ

SpinQ is a comprehensive quantum computing solutions provider dedicated to the commercialization and popularization of quantum computing.
SpinQ has established a comprehensive solutions layout through superconducting quantum computers, NMR(Nuclear Magnetic Resonance) quantum computers, quantum computing cloud platform, and application software.
SpinQ is empowering various cutting-edge fields such as scientific research, education, drug development, fintech, and artificial intelligence, aims to build scenario-based solutions that integrate quantum computing into diverse industries, making it a true productivity tool.
SpinQ Key Achievements on Quantum Hardware
SpinQ's Education-Grade NMR Quantum Computers
SpinQ is making quantum computing more accessible through the development of desktop quantum computers, portable quantum computers and quantum educational tools. Their solutions are designed to bring quantum experiments out of high-tech labs and into classroom settings. These systems typically leverage simplified quantum circuits that are ideal for educational and small-scale research purposes.
SpinQ Gemini Lab : A one-stop quantum computing platform focused on experimental teaching scenarios.
SpinQ Gemini : The world's first programmable desktop quantum computer.
SpinQ Gemini Mini/Mini Pro and SpinQ Triangulum Mini : The compact, portable quantum computers with a built-in touchscreen, control system, and curriculum for quantum teaching and self-learning.
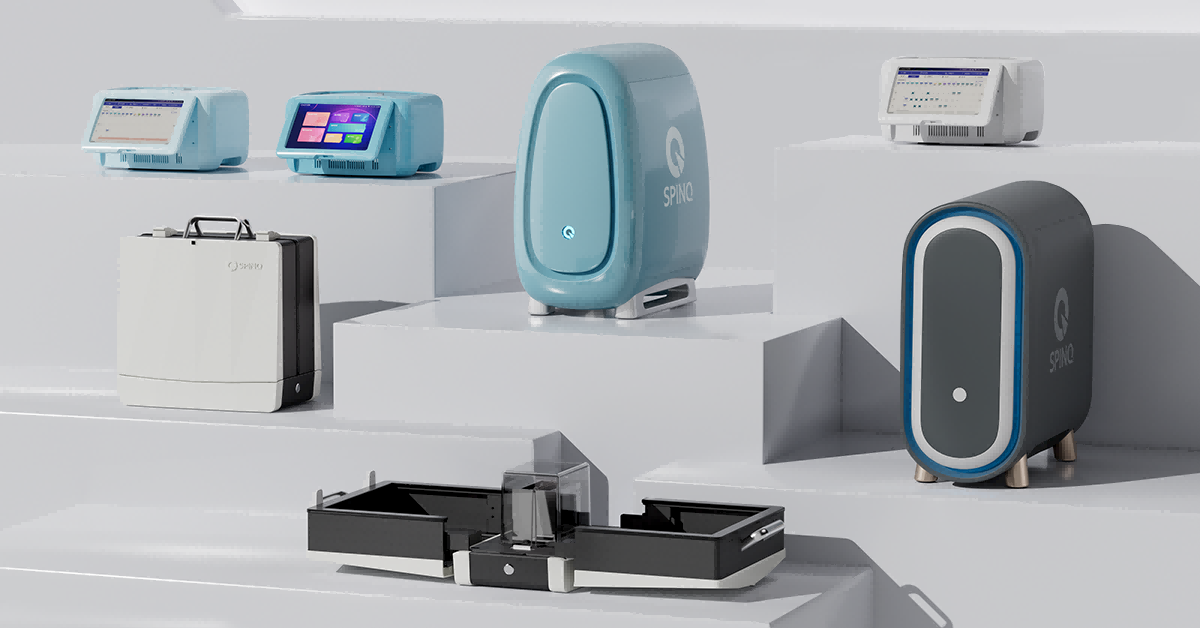

SpinQ's Industry-Grade Superconducting Quantum Computer
SpinQ's superconducting quantum computer employs circuits based on Josephson junctions, where qubits emerge from macroscopic quantum phenomena. This approach enables scalable qubit numbers, high gate fidelity, and controllable multi-qubit coupling, making it the fastest-evolving and most industrialized quantum computing technology
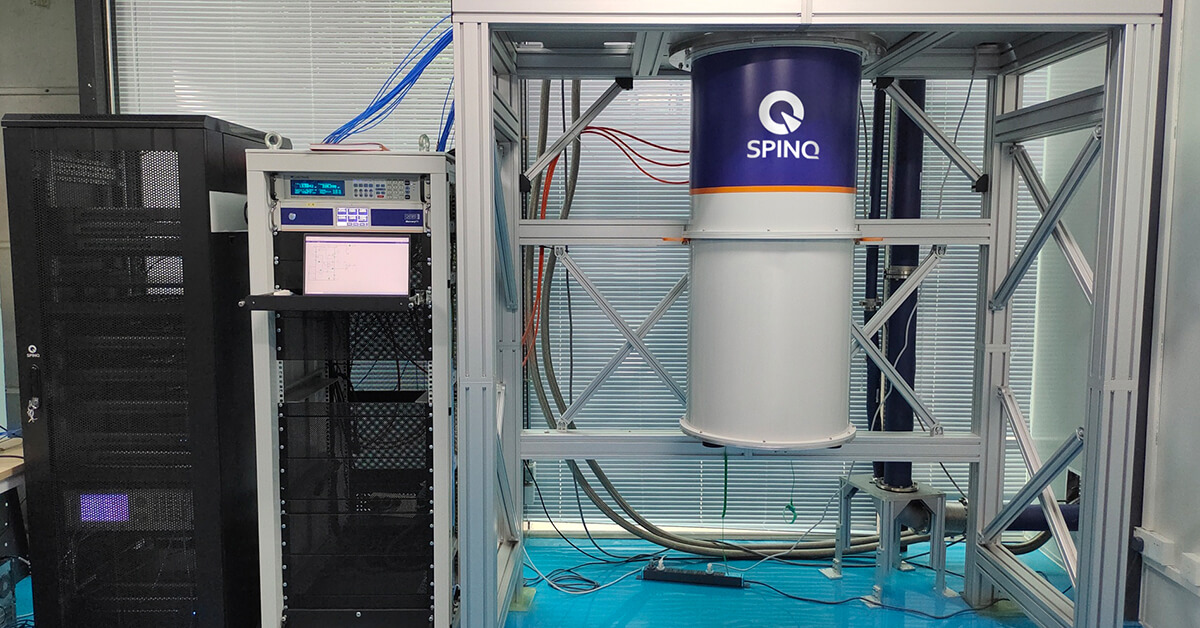

SpinQ's Superconducting QPU
SpinQ's superconducting QPUs feature a high Qi value, long qubit lifetime, and excellent stability, enabling qubits to maintain their quantum state for extended periods.
SpinQ has also delivered an independently developed superconducting quantum chip to a research institution in the Middle East, marking China's first export of such a chip abroad.
Additionally, SpinQ's proprietary QPU fabrication center offers QPU foundry services and custom quantum chip solutions.

SpinQ Key Achievements on Quantum Software
SpinQ Cloud: A universal quantum computing cloud platform
SpinQ QEDA: It is a highly automated superconducting QPU EDA design software, that generates quantum devices through parameterization and excellent automatic wiring algorithms.
SpinQit: A quantum computing programming framework that supports quantum programming based on Python.
By bridging the gap between academic theory and practical application, SpinQ has succeeded in democratizing quantum technology, especially in classroom and real-world industrial applications, furthering its mission to bring quantum computing to a broader audience.
#4 Microsoft
Microsoft is a key player in the quantum computing field, best known for its cloud-based platform, Azure Quantum. In addition to advanced quantum software, Microsoft is also developing quantum hardware based on topological qubits.
Microsoft Key Achievements on Quantum Hardware
Topological Qubits: Microsoft's quantum hardware strategy centers on the development of topological qubits, which are designed to be inherently resistant to errors. In September 2023, researchers from Azure Quantum presented evidence consistent with the creation and manipulation of Majorana quasiparticles for topological quantum computing.
Majorana 1 Chip: In February 2025, Microsoft unveiled Majorana 1, the world's first quantum processor powered by topological qubits. This breakthrough chip leverages a new class of materials called topoconductors, allowing precise control of Majorana particles to create more stable and reliable qubits. The Majorana 1 chip marks a critical milestone in Microsoft's mission to develop a scalable, fault-tolerant quantum computer.
Microsoft Key Achievements on Quantum Software
Microsoft has built a strong quantum software ecosystem, bringing together a large community of developers and researchers. This focus has made Microsoft a leader in quantum software development and innovation.
Azure Quantum Platform:
Microsoft's Azure Quantum is a comprehensive cloud-based platform that offers access to quantum computing resources, including quantum hardware from various providers including Quantinuum, lonQ, and Atom Computing, and a suite of development tools. The platform supports multiple quantum programming languages and provides a flexible environment for researchers and developers to experiment with quantum algorithms and applications.
Quantum Development Kit (QDK):
Microsoft's Quantum Development Kit (QDK) is a comprehensive toolset that includes the Q# programming language, along with libraries and tools for developing and simulating quantum applications. It also supports integration with other frameworks like Qiskit and Cirq.
It enables users to learn quantum computing concepts, build quantum programs, and run them on various supported quantum hardware backends. With seamless integration into Azure Quantum, the QDK also supports hybrid quantum-classical algorithms and offers features such as debugging and real-time feedback.
Q# Programming Language: To facilitate the development of quantum applications, Microsoft introduced Q#, a programming language specifically designed for expressing quantum algorithms. Q# integrates seamlessly with Microsoft's Visual Studio and Visual Studio Code, providing a familiar environment for developers to explore quantum programming.
You can write quantum programs in Q# using the Quantum Development Kit (QDK). Additionally, the QDK extension in Visual Studio Code enables direct submission of Q# programs to quantum hardware through an Azure subscription.
#5 Intel
Intel has been actively advancing quantum computing technology, leveraging its extensive experience in semiconductor manufacturing to develop scalable quantum solutions.
Intel's approach to quantum computing focuses on integrating quantum technologies with its existing silicon-based processes. By utilizing its cutting-edge 300-millimeter CMOS manufacturing techniques, Intel aims to create silicon spin qubits, facilitating the development of large-scale quantum computers.
Intel Key Achievements on Quantum Hardware
Tunnel Falls Quantum Chip:
In June 2023, Intel introduced "Tunnel Falls," a 12-qubit silicon quantum chip made available to the research community. This development chip serves as a platform for researchers to test and improve quantum algorithms and applications. Designed specifically for silicon spin qubits, it is fully integrated within Intel's Quantum Software Development Kit (QSDK), enabling seamless collaboration and testing by researchers.
Tunnel Falls is crucial for Intel's broader strategy of integrating quantum processors with control electronics on the same chip, simplifying the architecture of quantum systems and making them more scalable.
Advancements in Silicon Spin Qubits:
Intel has achieved exceptional yields in producing quantum dot arrays, demonstrating the potential for large-scale qubit production using advanced chip fabrication techniques, which aim to integrate quantum processors into conventional computing ecosystems. This progress is crucial for scaling quantum processors to the millions of qubits needed for fault-tolerant quantum computing.
Intel Key Achievements on Quantum Software
Intel Quantum SDK:
Intel released its Quantum Software Development Kit (SDK), a comprehensive quantum computing stack in simulation. It includes an LLVM*-based compiler extension providing intuitive C++ language extensions to program quantum algorithms.
The SDK provides an intuitive user interface, a compiler toolchain, and a quantum runtime environment optimized for hybrid quantum-classical algorithms. This platform enables developers to write and test quantum code in a simulated environment, preparing them for future quantum hardware implementations.
#6 Amazon Web Services (AWS)
Amazon's entry into quantum computing is through its cloud service, Amazon Braket, which provides researchers and businesses access to quantum hardware from various vendors. These include quantum annealers from D-Wave, ion-trap processors from IonQ, superconducting processors from Oxford Quantum Circuits and QuEra, as well as photonic quantum computers from Xanadu, along with its own Amazon Braket Quantum Simulator.
This enables experimentation with diverse quantum approaches without the high upfront cost of proprietary quantum systems.
Key Achievements of AWS in Quantum Software
Amazon Braket: Launched in 2020, Amazon Braket allows users to design, test, and run quantum algorithms on various quantum processors, including those based on superconducting qubits, trapped ions, neutral atoms and quantum annealers.
Claude 3 Integration: In September 2024, AWS integrated Claude 3, a large language model, with the Braket. This integration allows users to leverage advanced AI capabilities alongside quantum computing resources, enhancing the development and optimization of quantum algorithms.
Key Achievements of AWS in Quantum Hardware
Ocelot Quantum Chip: In February 2025, AWS unveiled Ocelot, a prototype quantum computing chip designed to enhance quantum error correction by up to 90%.
But so far Amazon has not yet developed its own fully operational quantum computer.
#7 IonQ
Founded in 2015, IonQ has rapidly emerged as a pioneer in trapped-ion quantum computing. Its systems have high gate fidelities and long coherence times.
The company continues to innovate, aiming to make quantum computing accessible and practical for a wide range of applications.
IonQ Key Achievements in Quantum Hardware
IonQ Forte Quantum Computer
In 2023, IonQ demonstrated a trapped-ion quantum computer called Forte with 36 qubits. It showcases all-to-all connectivity and high-fidelity operations. This achievement highlights the scalability potential of trapped-ion systems and represents a significant step toward building more powerful quantum processors.
It is available through all major quantum cloud providers like Microsoft's Azure Quantum and Amazon Braket.
IonQ Key Achievements in Quantum Software
IonQ Quantum Cloud is a platform that allows users to access IonQ's trapped-ion quantum computers through the cloud. It is also compatible with all major Quantum SDKs like Qiskit (IBM), Cirq (Google), and Q# (Microsoft Azure).
#8 Honeywell Quantum Solutions
Honeywell Quantum Solutions (HQS) has been a significant player in the quantum computing industry, focusing on developing quantum computers utilizing trapped-ion technology.
Honeywell System Model H1 : The System Model H1 quantum computer is based on trapped-ion technology. It has been available commercially since September 2020, the H1 features 10 high-fidelity qubits that are fully connected, allowing for more complex quantum circuits.
#9 Quantinuum (USA/UK)
In 2021, Honeywell Quantum Solutions merged with Cambridge Quantum to form Quantinuum.
This integration combines Honeywell's expertise in high-fidelity quantum hardware with Cambridge Quantum's proficiency in quantum software and algorithms, creating a comprehensive platform for advancing quantum technologies. Quantinuum continues to focus on trapped ion quantum computing.
Quantinuum Key Achievements in Quantum Hardware
System Model H1 (20 Qubits)
In June 2022, Quantinuum announced a major upgrade to its System Model H1, expanding it to 20 fully connected qubits. System Model H1 quantum computer is built with a single linear architecture and is divided into H1-1 and H1-2.
The H1-1 quantum computer features five gate zones, enabling it to perform multiple single-qubit and two-qubit gates in parallel. This parallelism allows users to execute complex algorithms without experiencing slowdowns.
The System Model H1-2 quantum computer becomes the first commercial quantum computer to pass Quantum Volume 4096, marking a significant performance benchmark in the industry.
System Model H2 (56 Qubits)
The System Model H2 is Quantinuum's latest quantum computer, designed with a racetrack architecture. It achieved a record quantum volume of 2,097,152.
High-Fidelity Operations
Quantinuum achieved a notable milestone by reaching "three 9's" (99.9%) two-qubit gate fidelity in its trapped-ion quantum computers, enhancing the reliability of quantum operations and paving the way for more complex computations.
Quantinuum Key Achievements in Quantum Software
TKET: TKET is an open-source quantum software toolkit that allows users to build quantum programs by combining quantum and classical operations using the pytket python interface.
LAMBEQ: LAMBEQ is an open-source library designed for developing models in language and cognitive science. It supports building end-to-end Quantum Natural Language Processing (QNLP) pipelines, working seamlessly with TKET.
Qermit: Qermit is a Python module that integrates with TKET, enabling users to apply and execute various error-mitigation protocols on quantum processors.
#10 D-Wave
D-Wave is a pioneering quantum computing company and has carved out a niche with its quantum annealing approach, a distinct method from traditional gate-based quantum computing.
Their systems are designed to solve specific classes of complex optimization problems, and D-Wave has been at the forefront of developing practical quantum computing solutions.
D-Wave Key Achievements in Quantum Hardware
Advantage Quantum Computer: In 2020, D-Wave introduced the Advantage system, featuring over 5,000 qubits and a new topology with 15-way qubit connectivity, significantly enhancing computational capabilities for complex optimization problem-solving.
Quantum Supremacy Demonstration: In March 2025, D-Wave announced a significant breakthrough by demonstrating quantum supremacy on a useful, real-world problem. Their annealing quantum computer successfully simulated complex magnetic materials in minutes—a task that would have taken classical supercomputers nearly one million years.
D-Wave Key Achievements in Quantum Software
The Leap™ Quantum Cloud Service: D-Wave offers quantum computing access through its Leap™ quantum cloud service, enabling developers and researchers worldwide to build and run quantum applications. This platform supports hybrid quantum-classical computing models, facilitating the integration of quantum computing into existing workflows.
Ocean™ Developer Tools: The Ocean SDK is a collection of open-source Python tools, provided by D-Wave Systems on their GitHub repository. It is designed to formulate and solve optimization problems using quantum annealing, bridging the gap between industry applications and quantum hardware.
#11 Xanadu
Xanadu is a Canadian quantum computing company founded in 2016. Xanadu specializes in photonic quantum computing, utilizing light particles (photons) to perform computations, which enables operations at room temperature and offers potential advantages in scalability and integration.
Xanadu Key Achievements in Quantum Hardware
Borealis Quantum Computer
In June 2022, Xanadu demonstrated quantum computational advantage using its programmable photonic quantum computer, Borealis.
Borealis, equipped with 216 squeezed-state qubits, utilizes advanced photonics and quantum light sources to generate squeezed-light pulses. As a publicly cloud-deployed quantum computer, Borealis is available to users worldwide through the Amazon Braket.
Aurora Quantum Computer
In January 2025, Xanadu introduced Aurora, the world's first scalable, networked, and modular quantum computer. Aurora consists of four modular and independent server racks that are photonically interconnected, comprising 35 photonic chips and 13 kilometers of fiber optics, all operating at room temperature. This 12-qubit machine represents a significant advancement in photonic quantum computing architecture.
Xanadu Key Achievements in Quantum Software
PennyLane: PennyLane is an open-source software library that integrates quantum computing with machine learning. It has become a widely used platform for quantum application development, providing a comprehensive library of tools, demonstrations, tutorials, and a vibrant community support forum. PennyLane facilitates research and the implementation of quantum algorithms across various domains, empowering users to develop quantum applications and program quantum computers with ease.
Catalyst: Catalyst is an experimental package that enables just-in-time (JIT) compilation of PennyLane programs, allowing entire quantum-classical workflows to be compiled and optimized.
Strawberry Fields: Strawberry Fields is an open-source, cross-platform Python library developed by Xanadu for designing, simulating, and executing programs on photonic quantum computers. It enables users to construct and simulate continuous-variable quantum photonic circuits and supports the development of photonic quantum algorithms.
#12 Quantum Circuits, Inc.
Quantum Circuits, Inc. (QCI) is a leading quantum computing company focused on superconducting circuits.
The company embraces the “correct first, then scale” philosophy, developing quantum processors designed to overcome decoherence challenges and solve optimization and machine learning problems.
Key Achievements of Quantum Circuits, Inc in Quantum Hardware
Aqumen Seeker Quantum Processing Unit
In November 2024, QCI introduced the Aqumen Seeker, an 8-qubit quantum processor utilizing dual-rail cavity qubits with built-in error detection. This design allows researchers and developers to achieve greater computational scale with fewer qubits, avoiding the need for brute-force methods.
Dual-Rail Qubits with Built-in Error Detection:
QCI has developed the industry's first dual-rail superconducting qubits featuring built-in error detection and control flow. This innovation addresses a critical obstacle in quantum computing by enabling precise error detection at the qubit level, paving the way for scalable error correction and consistent, reliable quantum computing results.
Key Achievements of Quantum Circuits, Inc in Quantum Software
Aqumen Cloud Service (ACS)
The Aqumen Cloud Service (ACS) is a cloud-based platform, also known as "Quantum-as-a-Service," that allows users to run, analyze, and explore quantum applications, offering a suite of tools for compiling, simulating, and executing quantum programs.
Aqumen SDK
The Aqumen SDK is a comprehensive toolkit consisting of Python libraries, documentation, and practical examples, enabling users to develop and execute quantum applications on Quantum Circuits QPUs and simulators. It seamlessly connects users to the Aqumen Cloud Service (ACS), with all submitted jobs easily monitored through the Cloud Portal.
Quantum Simulator by Quantum Circuits, Inc
Quantum Circuits offers a simulator that enables users to prototype and test quantum applications before deploying them on production quantum hardware, thereby broadening the accessibility and usability of quantum computing resources.
#13 PsiQuantum
PsiQuantum, founded in 2016 and headquartered in Palo Alto, California, is a quantum computing company committed to building a useful quantum computer with one million qubits, using a photonics-based architecture. However, it has not yet delivered a fully operational, fault-tolerant quantum system.
PsiQuantum Key Achievements in Quantum Hardware
Omega Photonic Chipset:
In February 2025, PsiQuantum announced Omega quantum photonic chipset designed specifically for utility-scale quantum computing.
This manufacturable chipset integrates advanced components necessary for constructing million-qubit quantum computers, marking a significant advancement in photonic quantum computing hardware.
#14 Infleqtion
Infleqtion, formerly known as ColdQuanta, is an emerging player in the quantum computing landscape, focusing on atom-based quantum technologies that advance sensing systems and quantum computing applications.
Infleqtion Key Achievements in Quantum Hardware
Quantum Components
Infleqtion manufactures a range of quantum components, including vacuum systems and processors designed to maintain ultra-cold atomic environments — a critical factor in reducing qubit motion and noise.
In addition, the company's offerings extend to quantum laboratory equipment, quantum radio frequency receivers, and advanced quantum positioning systems.
256 Neutral Atom Array Milestone:
Infleqtion achieved a significant breakthrough by creating a 16×16 neutral atom array, totaling 256 atoms—the largest of its kind in the UK. This advancement, part of the Scalable Quantum Atomic Lattice Computing Testbed (SQALE) project, represents a crucial step toward scalable quantum computing using neutral atom platforms.
Infleqtion Key Achievements in Quantum Software
Superstaq Platform: Superstaq is a quantum software platform designed to optimize the execution of quantum programs.
Quantum Material Design Application:
In December 2024, Infleqtion announced the delivery of its first quantum material science application powered by logical qubits. Through cloud integration with NVIDIA CUDA-Q, developers and researchers can now replicate Infleqtion's logical qubit experiments.
This accomplishment highlights the unique capability of Infleqtion's neutral atom quantum platform, which supports custom arrangements of qubit connections to optimize algorithm efficiency.
According to Infleqtion, this breakthrough achieved a 6x improvement in application-level computational accuracy.
#15 Quantum Computing Inc (QUBT)
Quantum Computing Inc. (QCi), is an innovative quantum computing company specializing in quantum optics and nanophotonic technology.
The company focuses on delivering accessible and affordable quantum solutions designed to operate at room temperature and low power, targeting applications in high-performance computing, artificial intelligence, cybersecurity, and remote sensing.
QCi has developed a novel approach called Entropy Quantum Computing, which utilizes quantum photonics devices for encoding and processing quantum information.
EQC is deeply rooted in the fascinating principles of quantum mechanics. Instead of trying to isolate and preserve perfect qubits, EQC embraces loss and decoherence — transforming entropy into a driving force for its quantum computing engine.
This approach eliminates the need for cryogenic or isolated housing. Moreover, EQC can be implemented using integrated photonics, enabling SWaP-C-friendly devices, just like regular PC's.
Key Achievements of Quantum Computing Inc in Quantum Hardware
Dirac-3 Entropy Quantum Computer: The Dirac-3 Entropy Quantum Computer is a nanophotonic machine designed to solve complex optimization problems. It offers powerful entropy computing capabilities and features capabilities such as binary optimization with over 11,000 qubits and integer optimization with over 1,000 qudits.
Key Achievements of Quantum Computing Inc in Quantum Software
Qatalyst Software Platform: QCi offers Qatalyst, a software package designed to solve complex business problems. It provides a REST API that can be programmed using various programming languages, such as Python, Ruby, or Java.
Quantum Random Number Generator: The company has developed a uniform probability distributed Quantum Random Number Generator (uQRNG) that utilizes quantum mechanics to generate truly random numbers.
#16 ALICE & BOB
ALICE & BOB is a French quantum computing startup. The company focuses on leveraging cat qubits to improve qubit stability and reduce error rates.
Cat qubits are a specialized form of superconducting qubit, inspired by Schrödinger's cat thought experiment. They leverage superpositions of coherent states to inherently suppress bit-flip errors, thereby offering the potential for improved error correction and fault-tolerant quantum computing.
So far the company has not yet built a fully functional quantum computer, but its mission is to build the first universal quantum computer, aiming to achieve this milestone by 2030.
ALICE & BOB Key Achievements in Quantum Hardware
Boson Chip: In 2024, the company achieved a significant milestone with the development of the Boson chip, the first cat qubit chip capable of handling quantum information with enhanced resilience against bit-flip errors.
Helium Chip Series: Building upon the Boson chip, the Helium chip lineup aims to create its first error-corrected logical qubit below the error-correction threshold, a crucial step toward fault-tolerant quantum computing.
Lithium: The chip series designed to scale multi-logical-qubit systems.
Beryllium: The chip series focused on enabling a universal set of logical gates.
Graphene: The chip series expected to deliver a quantum computer for industrial use cases by 2030.
ALICE & BOB Key Achievements in Quantum Software
Quantum Cloud Felis:
In November 2024, Alice & Bob unveiled Felis 1.0 — the industry's first logical qubit emulator — designed to support quantum scientists and developers in transitioning from noisy intermediate-scale quantum (NISQ) devices to future fault-tolerant quantum computing.
Integrated with IBM's Qiskit, Felis equips users with powerful tools to adapt algorithms for logical qubits and fine-tune them for fault-tolerant systems built on Alice & Bob's cat qubit architecture.
#17 Atom Computing
Atom Computing is a pioneering quantum computing company specializing in the use of neutral atoms as qubits. This approach shows promise in scalability and inherent noise resilience.
Key Achievements of Atom Computing in Quantum Hardware
Exceeding 1,000 Qubits: In October 2023, Atom Computing achieved a significant milestone by developing a quantum computing platform with a 1,225-site atomic array populated with 1,180 qubits. This accomplishment marked the first time a company had surpassed the 1,000-qubit threshold for a universal gate-based system.
Microsoft and Atom Computing have collaborated and made significant progress in quantum computing by creating and entangling 24 logical qubits using neutral atoms. They have also demonstrated error detection, correction, and computation with 28 logical qubits. Together, the companies have developed a commercial quantum machine built with these advanced logical qubits, integrated with Microsoft's qubit-virtualization system and Azure Elements
#18 QuEra Computing
QuEra Computing specializes in neutral-atom quantum computing, utilizing Rydberg atom technology to construct scalable quantum systems. Their architecture is designed to enhance qubit interactions, offering reconfigurable connectivity and extended coherence times, while striving to minimize cross-talk.
Key Achievements of QuEra Computing in Quantum Hardware
Aquila: 256-Qubit Analog Quantum Computer
Aquila, launched in November 2022 and developed by QuEra, is the world's largest publicly available quantum computer, built on groundbreaking research from Harvard and MIT. It features 256 neutral-atom qubits and is accessible via Amazon Braket.
Advancements in Quantum Error Correction
In collaboration with institutions like Harvard, MIT, NIST, and the University of Maryland, QuEra has successfully performed complex error-corrected quantum algorithms on 48 logical qubits, marking a significant step toward scalable and fault-tolerant quantum systems.
#19 Atos and Eviden
Atos SE is a French multinational information technology service and consulting company. Atos is a recognized player in quantum computing, offering solutions like the "Atos Quantum Learning Machine (QLM)" as an on-premises hardware environment to simulate and develop quantum software.
In 2023, Atos restructured its operations, resulting in the creation of Eviden, a subsidiary focused on advanced computing, cloud, and digital security services.
Atos's Contributions to Quantum Computing
Quantum Learning Machine (QLM):
Atos developed the QLM, a high-performance simulator that enables users to design, test, and execute quantum algorithms on classical supercomputers. This tool supports the exploration of quantum applications without immediate access to quantum hardware.
Eviden's Initiatives in Quantum Computing
Qaptiva HPC:
Eviden introduced Qaptiva HPC, a software that enhances the computational capabilities of your HPC cluster by incorporating quantum emulation. It boosts the performance of large-scale simulations, enabling faster and more efficient research breakthroughs.
myQLM – Quantum Python Package:
myQLM, developed by Eviden, is a quantum software stack that enables the creation, simulation, optimization, and execution of quantum programs.
Quantum Computing Consulting Services:
Eviden offers specialized consulting services to assist businesses in integrating quantum computing solutions into their operations, guiding them through the complexities of quantum technology adoption.
Collaboration with IQM:
Eviden partnered with IQM to install a quantum computer, aiming to bolster its quantum capabilities and provide clients with access to advanced quantum resources.
In summary, Atos and Eviden, as entities within the Atos Group, have both contributed to the quantum computing field. Atos focuses on quantum algorithm simulation through Quantum Learning Machine (QLM), while Eviden emphasizes consulting, software solutions, and collaborations aimed at integrating quantum technologies into business applications.
#20 QC ware
QC Ware is a Quantum-as-a-Service (QaaS) company that leverages quantum computing technologies to develop enterprise solutions aimed at solving complex computational challenges across various industries.
By providing advanced algorithm development and optimization tools, QC Ware enables the integration of quantum computing solutions into existing business workflows, accelerating the transition from research to real-world applications.
Key Achievements of QC Ware in Quantum Software
Promethium: Quantum Chemistry Software & Platform
Promethium, the GPU-powered chemistry simulation platform, is QC Ware's flagship product.
It leverages quantum-inspired algorithms to elevate computational chemistry and accelerate the discovery of pharmaceuticals, chemicals, and materials.
It delivers unprecedented speed and accuracy in molecular modeling, enabling researchers to conduct large-scale simulations efficiently. Promethium is hosted on AWS for easy integration into cloud environments.
Forge
Forge is a cloud-based platform that provides turn-key algorithm implementations for data scientists, financial analysts, and engineers. It allows users to explore problems in binary optimization, machine learning, and linear algebra on both simulators and real quantum hardware.
#21 NVIDIA
Founded in 1993, NVIDIA is known for its leadership in graphics processing units (GPUs) for gaming, professional visualization, data centers, and artificial intelligence (AI) applications.
In quantum computing, NVIDIA is advancing the field with its Quantum Computing Platform and software stack. Through these efforts, the company aims to integrate quantum technologies with its strengths in AI and supercomputing to drive innovation across industries.
At the recent GPU Technology Conference (GTC) in March 2025, NVIDIA announced the establishment of the Accelerated Quantum Research Center (NVAQC) in Boston, dedicated to developing quantum computing architectures and algorithms.
The NVIDIA Accelerated Quantum Research Center (NVAQC) aims to integrate quantum hardware with AI supercomputers, driving the development of accelerated quantum supercomputing. By combining the strengths of quantum and classical computing, the center focuses on addressing key challenges in the field, such as reducing qubit noise and transforming experimental quantum processors into practical, reliable devices.
NVIDIA Key Achievements in Quantum Software
cuQuantum
NVIDIA cuQuantum is an SDK offering a suite of libraries and tools designed to accelerate quantum computing simulations on classical hardware.
The cuQuantum SDK includes components such as cuStateVec, which facilitates efficient state vector computations, and cuTensorNet, which supports tensor network computations. These tools enable researchers to simulate complex quantum circuits and optimize quantum operations effectively.
It helps bridge the gap between quantum hardware capabilities and practical software applications.
NVIDIA Quantum Cloud
NVIDIA Quantum Cloud is a dedicated platform for quantum developers, offering powerful tools and resources to build and test quantum algorithms. Through its APIs, developers can run CUDA-Q™ projects on NVIDIA's GPU systems, enabling advanced quantum simulation and fostering collaboration in quantum software development.
Through collaborations with quantum research institutions and companies, NVIDIA is playing a significant role in bridging the gap between classical and quantum computing, making quantum technologies more accessible and usable for a wide range of industries.
#22 Toshiba
Toshiba, founded in 1875, is a prominent Japanese multinational conglomerate specializing in various sectors, including electronics, energy, and infrastructure.
In the realm of quantum computing, Toshiba has been a pioneer, particularly in quantum cryptography and quantum-safe communication technologies.
Key Achievements of Toshiba in Quantum Computing
Quantum Key Distribution (QKD) Systems
Toshiba's Quantum Key Distribution (QKD) systems utilize quantum physics principles to secure network communications, safeguarding sensitive information against potential quantum computing threats and ensuring data confidentiality and integrity.
These systems have demonstrated the capability to transmit keys over standard telecom fiber links exceeding 100 kilometers, significantly enhancing communication security.
#23 Fujitsu
Fujitsu, established in 1935, is a leading Japanese multinational information and communications technology (ICT) company. It offers a wide range of computing devices, storage solutions, and ICT services, positioning itself as a global player in the IT industry.
In the realm of quantum computing, Fujitsu has been actively engaged in both quantum hardware and software developments.
In 2017, Fujitsu unveiled the Digital Annealer, a quantum-inspired digital architecture designed to solve complex combinatorial optimization problems. While not a quantum computer in the strictest sense, it employs principles of quantum mechanics, particularly quantum annealing, to solve problems much faster than traditional computers.
In 2023, in collaboration with RIKEN, Fujitsu introduced Japan's first 64-qubit superconducting quantum computer. Additionally, Fujitsu has developed a hybrid quantum computing platform that optimally links a 64-qubit superconducting quantum computer with a 40-qubit quantum simulator.
Featured Content





.png)