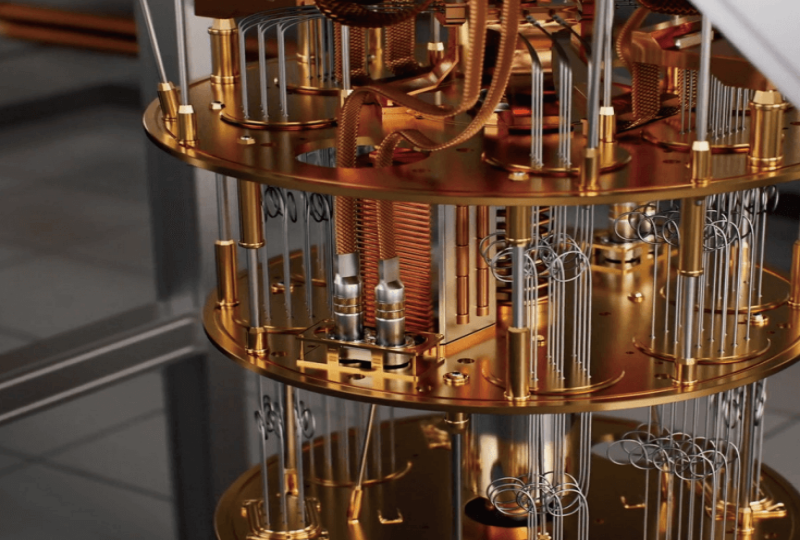
Quantum Computing Computer: How It Works & Why It Matters
2025.02.09 · Blog
A quantum computing computer is a groundbreaking machine that processes information in ways that classical computers cannot. By harnessing the principles of quantum mechanics—such as superposition, entanglement, and quantum gates—these computers can solve complex problems exponentially faster than traditional systems.
This article explores what makes quantum computing computers unique, how they function, and their potential impact on various industries.
What Is a Quantum Computing Computer?
A quantum computing computer is a specialized system that uses qubits (quantum bits) instead of classical binary bits. Unlike traditional computers, which process data as either 0s or 1s, quantum computers leverage qubits that can exist in multiple states simultaneously. This allows them to perform vast calculations in parallel, significantly enhancing computational efficiency.
Quantum Computing Computer VS Classical Computers: Key Differences
| Feature | Classical Computer | Quantum Computing Computer |
| Data Unit | Bit (0 or 1) | Qubit (0, 1, or both) |
| Processing Power | Sequential | Parallel (Superposition) |
| Connectivity | Independent Bits | Entangled Qubits |
| Error Sensitivity | Low | High (requires correction) |
How Does a Quantum Computing Computer Work?
1. Superposition
Qubits can be in a state of 0, 1, or both at the same time, allowing quantum computers to explore multiple possibilities simultaneously.
2. Entanglement
When qubits become entangled, their states become interconnected. This means changing one qubit's state instantly affects its entangled partner, enabling faster information processing.
3. Quantum Gates
Quantum computers use quantum gates (such as Hadamard and CNOT gates) to manipulate qubit states, enabling complex computations that are impossible for classical logic gates.
Applications of Quantum Computing Computers
Quantum computing computers have the potential to revolutionize industries, including:
Cryptography: Breaking modern encryption or developing ultra-secure quantum cryptography.
Drug Discovery: Simulating molecular interactions to accelerate pharmaceutical research.
Artificial Intelligence: Enhancing machine learning models with faster data analysis.
Financial Modeling: Optimizing stock portfolios, risk analysis, and fraud detection.
Optimization Problems: Improving logistics, supply chain management, and traffic flow solutions.
Challenges and Future Prospects of Quantum Computing Computers
Error Correction: Qubits are highly sensitive to external noise, requiring complex error-correction techniques.
Scalability: Increasing the number of stable qubits remains a challenge for researchers.
Hardware Limitations: Maintaining qubits at near-absolute-zero temperatures demands advanced engineering solutions.
Leading companies like Google, IBM, Microsoft, and SpinQ are actively developing quantum computing computers, aiming to achieve practical quantum advantage.
Conclusion
A quantum computing computer represents a paradigm shift in computational power, offering solutions to problems that classical computers struggle to address. While challenges remain, advancements in quantum technology are paving the way for a new era of computing.
As research progresses, quantum computing computers will become more accessible, unlocking groundbreaking innovations across industries. Stay tuned—the future of computing is quantum!
Featured Content
Popular Reads




.png)