What is a Superconducting Quantum Processor? Explained
2025.03.03 · Blog
Superconducting quantum processors are at the forefront of quantum computing technology, playing a key role in unlocking the full potential of quantum computers. These processors are designed using superconducting circuits, which offer significant advantages over classical computers.
In this article, we'll explain how superconducting quantum processors work, their benefits, and their applications in various industries.
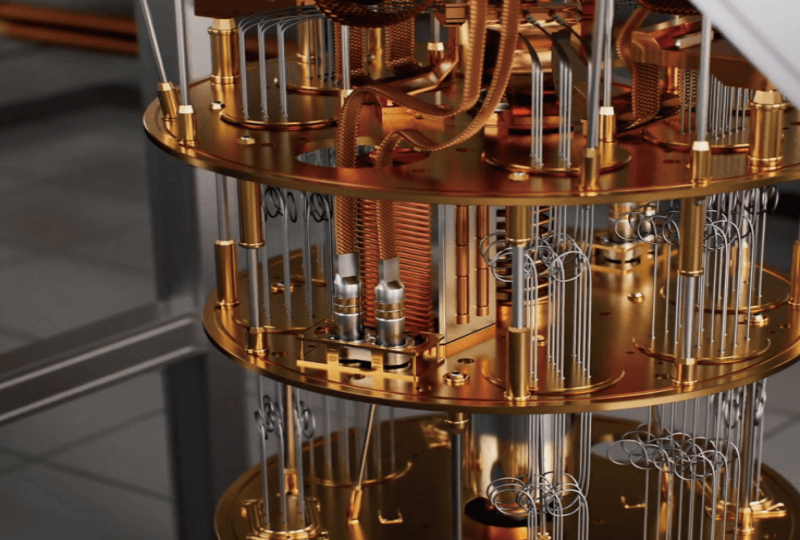
What is a Superconducting Quantum Processor?
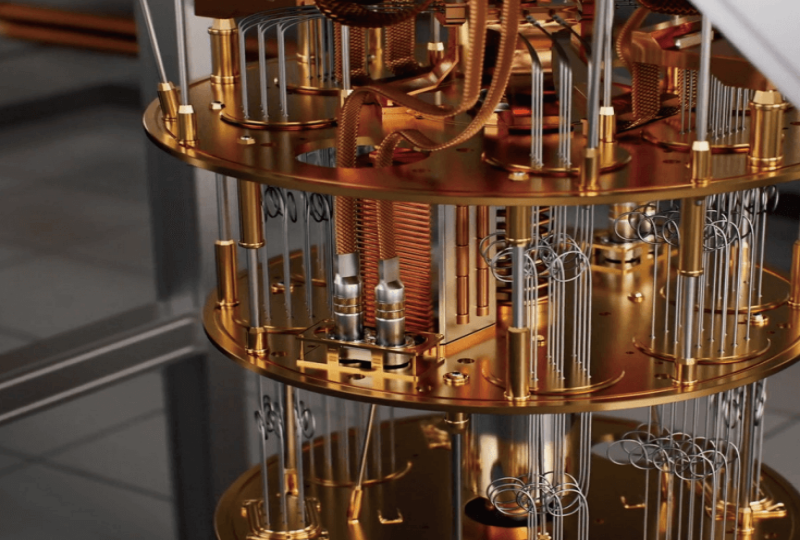
A superconducting quantum processor is a device used in quantum computers that operates using superconducting circuits. These circuits are made from materials that can conduct electricity without resistance when cooled to extremely low temperatures. The quantum processor uses quantum bits, or qubits, to store and manipulate information.
Unlike classical bits, which are either 0 or 1, qubits can exist in multiple states simultaneously due to quantum superposition. This allows superconducting quantum processors to perform complex calculations much faster than traditional computers.
How Do Superconducting Quantum Processors Work?
Superconducting quantum processors rely on Josephson junctions, which are thin insulating layers sandwiched between two superconducting materials. These junctions create quantum interference, enabling the processor to function as a quantum bit. When quantum algorithms are applied, these qubits can interact and entangle, performing calculations that are impossible for classical systems.
To function, these processors require a stable environment with extremely low temperatures, typically achieved with dilution refrigerators. The superconducting circuits are shielded from electromagnetic interference, ensuring the quantum system remains coherent for long enough to perform computations.
Advantages of Superconducting Quantum Processors
Scalability: Superconducting quantum processors are highly scalable, allowing for the addition of more qubits to increase computational power.
Speed: The speed of quantum operations far exceeds that of classical computers, providing enormous potential for solving complex problems.
Robustness: These processors are relatively more robust to noise and errors, making them a practical choice for real-world quantum computing applications.
Applications of Superconducting Quantum Processors
Superconducting quantum processors are making a significant impact across various industries:
Quantum Simulation: These processors enable the simulation of complex quantum systems, useful in fields like chemistry and material science.
Machine Learning: Quantum processors can accelerate certain machine learning tasks by handling vast amounts of data at once.
Optimization: They are useful for solving optimization problems in areas like logistics, finance, and artificial intelligence.
Cryptography: Superconducting processors are key to developing quantum cryptography solutions that could revolutionize cybersecurity.
Challenges and Future of Superconducting Quantum Processors
While superconducting quantum processors show great promise, there are challenges to overcome. Cooling the system to ultra-low temperatures is energy-intensive and costly. Additionally, maintaining qubit coherence and reducing errors in quantum operations remain key research areas.
The future of superconducting quantum processors looks bright, with ongoing advancements aimed at improving stability, error correction, and scalability. As quantum hardware becomes more efficient and accessible, the full potential of quantum computing will be realized, impacting industries worldwide.
Conclusion
Superconducting quantum processors are at the heart of quantum computing's potential to revolutionize technology. With their ability to perform operations beyond the reach of classical systems, they hold the promise of breakthroughs in various fields, from material science to artificial intelligence. As technology continues to evolve, these processors are paving the way for the next generation of computational power.
Featured Content
Popular Reads




.png)