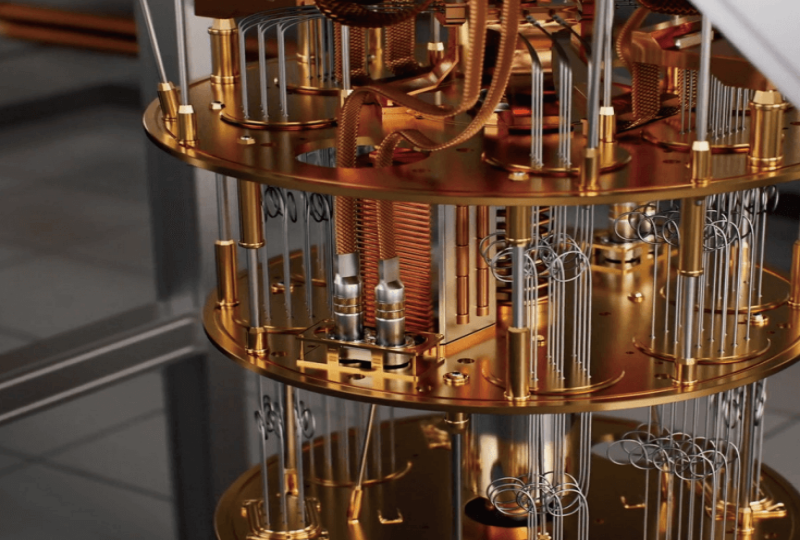
What is a Real Quantum Computer? Explained Simply
2025.02.26 · Blog
As quantum computing continues to capture the world’s attention, many are left wondering: what exactly is a real quantum computer? While the concept of quantum computing has been around for years, it’s only recently that we’ve begun to see tangible progress. In this article, we will explain what a real quantum computer is, how it works, and what makes it different from traditional computing systems.
What Makes a Quantum Computer "Real"?
At its core, a real quantum computer is a machine that uses quantum mechanics principles, such as superposition and entanglement, to perform calculations in ways that classical computers cannot. Unlike classical computers, which use bits as the smallest unit of data (either 0 or 1), a quantum computer uses qubits.
Qubits can exist in multiple states simultaneously, thanks to superposition, allowing them to perform multiple calculations at once. This enables quantum computers to solve complex problems much faster than classical systems.
The Power of Qubits
The key differentiator of a real quantum computer is its reliance on qubits. A qubit can represent both 0 and 1 at the same time, unlike a classical bit, which is restricted to one state. This unique property, coupled with entanglement (where qubits are linked and can affect each other even over vast distances), allows quantum computers to perform calculations on a much larger scale and in parallel.
Real-World Applications of Real Quantum Computer
While we’re still in the early stages, real quantum computers have the potential to revolutionize various industries:
Drug Discovery: Quantum computers can simulate molecular structures, speeding up drug development.
Optimization: Quantum computing is used to solve complex optimization problems, such as supply chain logistics and portfolio management.
Cryptography: Quantum computers can break traditional encryption methods, leading to the development of more secure systems.
Challenges in Building Real Quantum Computers
Despite their promising potential, real quantum computers face several challenges:
Decoherence: Qubits are extremely sensitive to environmental interference, making it hard to maintain their state long enough to perform calculations.
Error Correction: Quantum computers require robust error-correction techniques to ensure accurate computations.
Scalability: Scaling up quantum systems to handle complex tasks is still a significant hurdle.
Conclusion
A real quantum computer is not just a theoretical concept but an emerging reality with immense potential. With ongoing advancements in quantum hardware, we are one step closer to solving some of the world’s most complex problems. Whether in drug discovery, optimization, or cryptography, the future of computing lies in the realm of quantum mechanics. As quantum technologies continue to evolve, the line between classical and quantum computing will blur, bringing us closer to a new era of computing power.
Stay tuned to the latest developments in quantum computing as the race for building fully functional real quantum computers heats up.
Featured Content
Popular Reads




.png)