Top 18 Quantum Computer Companies [2025 Updated]
2025.03.07 · Blog
Looking for the top quantum computer manufacturers? You're in the right place!
In this guide, we cover 18 leading quantum computer manufacturers, showcasing their cutting-edge technologies, quantum hardware innovations, and how they are shaping the future of quantum computing.
Whether you're a researcher, investor, or quantum enthusiast, this article will help you discover the quantum computing companies building the quantum machines transforming industries — from finance and pharmaceuticals to logistics, cryptography, and AI.
What Are Quantum Computers?
Quantum computers utilize quantum bits, or qubits, which can represent both 0 and 1 simultaneously through a phenomenon known as superposition. This capability enables quantum computers to solve certain problems much faster than classical computers. To achieve this, quantum computers rely on various quantum technologies such as superconducting qubits, trapped ions, and photonics, all of which are being developed and manufactured by different companies worldwide.
#1 IBM (USA)
IBM is a global leader in quantum computing, with a strong focus on superconducting quantum computers. The company has made remarkable advancements in quantum hardware, software, and services.
IBM's quantum processors, powered by superconducting qubits, are at the core of its innovation, driving the development of scalable quantum systems. In this section, we highlight some of IBM's key achievements in quantum computers.
Key Quantum Computers from IBM:
1. IBM Quantum Hummingbird:
The Hummingbird processor, introduced in 2020, marked a major milestone for IBM as it featured 65 qubits, a significant step toward larger, more capable quantum systems. This processor set the stage for IBM's subsequent advancements in quantum technology.
2. 127-Qubit Eagle Quantum Processor:
Released in 2021, the Eagle processor made IBM the first company to create a 127-qubit quantum processor. Eagle's design pushed the boundaries of quantum error correction and improved qubit connectivity, moving closer to fault-tolerant quantum computing.
3. 433-Qubit Osprey Quantum Processor :
IBM unveiled the Osprey processor in 2022, boasting 433 qubits. Osprey is a crucial step in scaling up quantum computing systems and is designed to handle more complex calculations, bringing us closer to practical quantum applications.
4. 1,121-Qubit Condor Quantum Processor:
Condor, a 1,121 superconducting qubit quantum processor based on cross-resonance gate technology represents a substantial leap in terms of qubit count, positioning IBM at the forefront of the race to develop larger and more powerful quantum computers.
5. IBM Quantum System One:
IBM's Quantum System One, introduced in 2019, is a commercially available quantum computer designed for enterprise use. It features an integrated quantum system that's accessible to clients, offering them the ability to experiment with and harness quantum computing for real-world applications.
6. IBM Quantum System Two & IBM Quantum Heron R2 Processor:
IBM Quantum System Two, with its advanced architecture, builds on the lessons learned from previous systems and aims to deliver increased coherence times and qubit connectivity. The Heron R2 processor is expected to provide enhanced performance for more sophisticated quantum applications.
IBM's Future Quantum Computing Roadmap:
Looking ahead, IBM has ambitious plans for the future of quantum computing:
Kookaburra Processor (2025): In 2025, IBM plans to unveil the Kookaburra processor, which will feature 1,386 qubits in a multi-chip configuration. This processor will introduce quantum communication links, enabling multiple chips to work together seamlessly. IBM aims to connect three Kookaburra chips, forming a 4,158-qubit quantum system.
Quantum-Centric Supercomputer (2033): By 2033, IBM envisions the development of a quantum-centric supercomputer with 100,000 qubits.
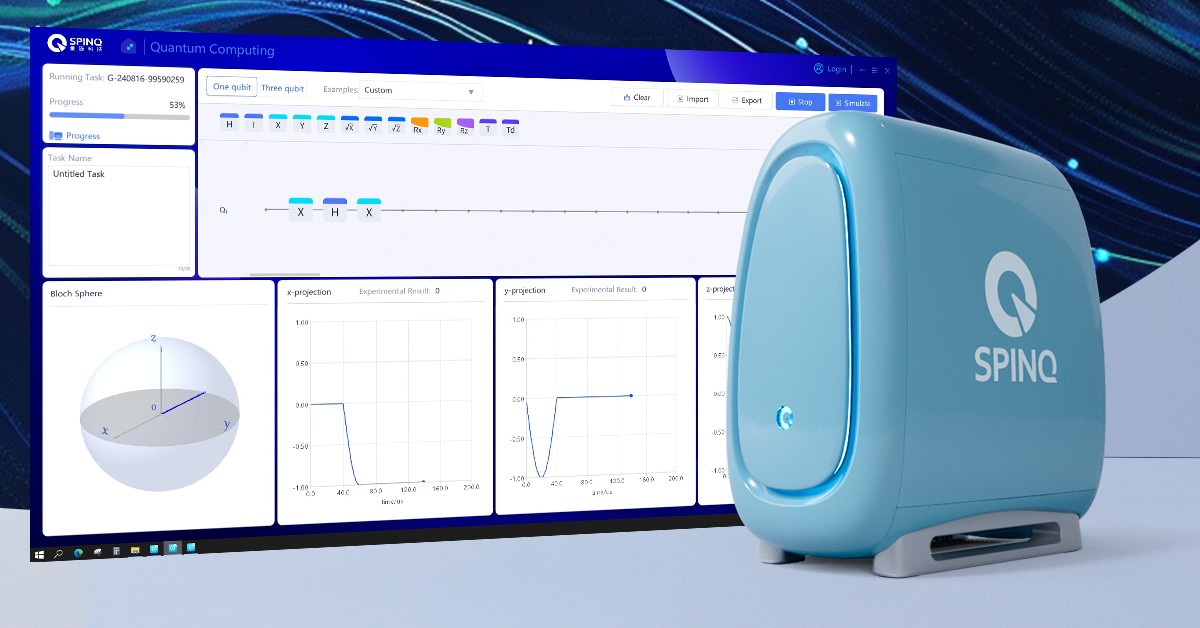
#2 SpinQ (China)

SpinQ is a leading quantum computer manufacturer, specializing in both industry-grade superconducting quantum computers and education-grade NMR (Nuclear Magnetic Resonance) quantum computers.
By bridging the gap between cutting-edge quantum technology and real-world applications, SpinQ is making quantum computing accessible across industries like finance, drug development, and quantum education and research.
Committed to the industrialization and widespread adoption of quantum computing, SpinQ is focused on making quantum systems truly productive, practical, and useful.
As the first Chinese company to export quantum computing products internationally, SpinQ's quantum computers are now used in over 30 countries and regions worldwide.
Also read:
SpinQ Powers OsloMet University's Development in Quantum Education, Research, and Science Outreach
Colombia's First Quantum Computer: Advancing Education, Research, and Technological Innovation
Key Quantum Computers from SpinQ:
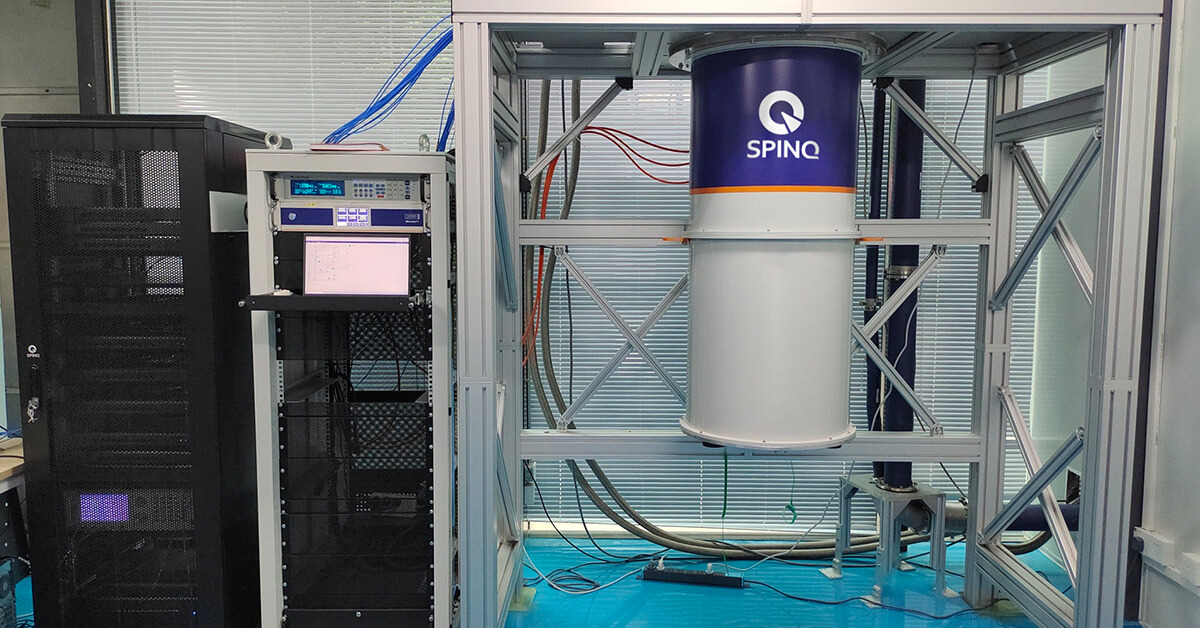
1. SpinQ Superconducting Quantum Computer
SpinQ Superconducting Quantum Computer leverages circuits with Josephson junctions, where qubits are formed by macroscopic quantum effects. This method offers scalable qubit numbers, high gate fidelity, and controllable multi-qubit coupling, making it the most rapidly advancing and industrialized quantum computing technology in use today.

2. SpinQ Gemini Mini/Mini Pro: 2-qubit Portable NMR Quantum Computer
The SpinQ Gemini Mini and Mini Pro provide a comprehensive solution for quantum computing education and demonstrations. Featuring a built-in touchscreen, control system, and curriculum for quantum teaching and self-learning, they enable users with diverse academic backgrounds to quickly understand the fundamentals of quantum computing and algorithm design.

3. SpinQ Triangulum Mini: 3-qubit Portable NMR Quantum Computer
With an improved pulse scheme, the SpinQ Triangulum Mini offers a more stable experimental process, supporting a broader range of quantum computing experiments and more advanced design requirements.

4. SpinQ Gemini: 2-qubit Desktop NMR Quantum Computer
Based on a 2-qubit real quantum computing design, the SpinQ Gemini allows users to perform operations with hundreds of single-qubit gates or dozens of two-qubit gates using software. It provides an intuitive interface that displays the quantum computing process and results, offering a flexible and comprehensive platform for experimental design, making it ideal for education and demonstrations.

5. SpinQ Triangulum: 3-qubit Desktop NMR Quantum Computer
The SpinQ Triangulum provides a complete solution for quantum computing education and demonstrations. It supports all 3-qubit quantum algorithms, allowing users to write their own quantum programs. It also features open hardware-level pulse sequence editing. Cost-effective, maintenance-free, and highly stable, it is designed for ease of use and long-term reliability.
#3 Google Quantum AI (USA)
Google Quantum AI is a leader in quantum computing, specializing in the development of superconducting qubit-based quantum computers. Google is at the cutting edge of advancing quantum algorithms, particularly for applications in artificial intelligence, machine learning, cryptography, and optimization.
Google's quantum computing division combines quantum hardware, software, and algorithms to drive quantum advancements and make them commercially viable.
Key Quantum Computers from Google:
1. Bristlecone
Bristlecone was one of Google's early breakthroughs in quantum computing in 2017. Designed as a testbed for quantum algorithms, it featured 72 qubits, offering a stepping stone to more powerful processors. Bristlecone laid the groundwork for future innovations and was critical in proving the potential of superconducting qubits for large-scale quantum computing.
2. Sycamore Quantum Processor
Google's Sycamore processor made headlines in 2019 when it achieved quantum supremacy by solving a complex problem in 200 seconds, a task that would take classical supercomputers thousands of years to complete. With 53 operational qubits (originally designed with 54 qubits, but only 53 were functional during the experiment), Sycamore demonstrated the power of quantum computing in solving real-world problems, such as running chemical simulations and modeling wormholes, establishing Google as a leader in the field.
3. Willow Chip
Launched by Google in late 2024, the Willow chip features 105 superconducting qubits and focuses on advancing quantum error correction (QEC), a critical challenge in quantum computing. Quantum systems are highly susceptible to errors caused by decoherence and noise, and Willow addresses this by enabling more efficient error handling.
This improvement enhances the reliability of quantum processors, allowing for more stable and accurate execution of quantum algorithms. With its increased qubit capacity, Willow can process more complex quantum circuits, paving the way for practical applications in fields such as chemistry, material science, and optimization.

#4 Microsoft (USA)
Microsoft offers a comprehensive suite of tools for developing quantum applications, with its most notable advancement being the Azure Quantum platform. This platform integrates quantum hardware from various manufacturers, including partners like IonQ and Quantinuum, allowing users to experiment with different quantum computing approaches. Through the platform, users can also develop, test, and deploy quantum algorithms in the cloud.
A key focus of Microsoft's quantum computing efforts is the development of topological qubits. Microsoft believes that topological qubits are essential for scaling up quantum computers to a practical and commercially viable level, and they are actively working to advance this technology as part of their long-term quantum roadmap.
By prioritizing topological qubits, Microsoft aims to enhance stability, reduce noise, and develop scalable, fault-tolerant quantum systems.
Majorana 1 Chip:The world's first quantum processor powered by topological qubits
In February 2024, Microsoft unveiled its latest milestone in quantum computing: the Majorana 1 chip. This chip represents a significant step in the development of topological qubits, which are designed to be more robust and scalable than conventional qubits.
The release of the Majorana 1 chip marks a crucial advancement toward Microsoft's goal of developing a fully scalable and fault-tolerant quantum computer.
#5 Intel (USA)
Intel is a leading semiconductor manufacturer. The company began exploring quantum computing in the early 2000s, researching both quantum theory and hardware to address the limitations of classical silicon-based transistors.
Intel is particularly focused on silicon-based quantum processors, specifically developing spin qubits using silicon — a technology in which the company has extensive expertise. This approach not only offers scalability but also ensures compatibility with existing semiconductor manufacturing processes. By leveraging its advanced silicon manufacturing capabilities, Intel aims to create quantum processors that are easier to produce at scale, thereby meeting the demands of real-world applications
It's worth noting that Intel has not yet developed a fully functioning, commercial quantum computer. The company has made progress in developing quantum processors, but they are still in the research and development phase.
Key Quantum Chips from Intel
1. Tangle Lake chip:
Intel's Tangle Lake was their first quantum processor based on silicon, a 49-qubit superconducting quantum processor.
This chip leverages Intel's extensive experience with silicon-based technologies, which makes it more compatible with classical semiconductor manufacturing processes.
2. Horse Ridge II Cryogenic Control Chip
The Horse Ridge II cryogenic control chip is designed to improve the operation of quantum processors by reducing complexity.
This chip integrates cryogenic electronics directly into the quantum processor, helping to improve scalability by making the quantum computing systems more manageable.
3. Tunnel Falls chips
Intel's Tunnel Falls chip, a 12-qubit silicon chip, represents a critical step forward in spin-based quantum dot quantum systems. These quantum dots, semiconductor devices that can trap individual electrons, are being explored for their potential in quantum information processing.
Tunnel Falls is crucial for Intel's broader strategy of integrating quantum processors with control electronics on the same chip, simplifying the architecture of quantum systems and making them more scalable.
#6 Honeywell Quantum Solutions (USA)
Honeywell is a key player in quantum computing, utilizing trapped-ion technology for its quantum systems. Their quantum computers are available on quantum cloud platforms like Microsoft Azure and Amazon Braket.
Honeywell's quantum system features ion qubits controlled by an advanced system that reads out qubit states and executes operations, ensuring quantum computations are performed with high accuracy and reliability.
In a significant move, Honeywell merged with Cambridge Quantum Computing, forming Quantinuum. This partnership combines Honeywell's hardware expertise with Cambridge Quantum's software and algorithmic capabilities, accelerating progress toward practical quantum computing solutions.
Honeywell System model H1
Honeywell has introduced the System Model H1, its latest quantum computer based on trapped-ion technology. Available commercially since September 2020, the H1 features 10 high-fidelity qubits that are fully connected, allowing for more complex quantum circuits. It also supports mid-circuit measurement to reduce the qubits needed for some algorithms and includes qubit reuse, which enhances efficiency in quantum computations.
#7 Quantinuum (USA/UK)
Founded in 2021, Quantinuum was formed by the merger of Cambridge Quantum Computing (CQC), known for its quantum software development, and Honeywell Quantum Solutions, expertise in building trapped-ion based quantum hardware. The company also provides research partnerships, enabling customers to access and leverage its cutting-edge quantum technologies.
Quantinuum focuses on trapped-ion quantum computers, offering all-to-all qubit connectivity to ensure high-quality quantum states. This distinct approach enables Quantinuum to drive innovations in quantum chemistry, cybersecurity, natural language processing, and machine learning.
In April 2024, the company's H-Series trapped-ion quantum computers reached a quantum volume of 1,048,576, marking the highest achievement to date.
Key Trapped Ion Quantum Computers from Quantinuum
1. System Model H1
In June 2022, Quantinuum announced a major upgrade to its System Model H1, expanding it to 20 fully connected qubits and boosting its capacity for concurrent quantum operations. The enhancement also increased the number of gate zones from three to five, enabling the H1-1 system to execute more quantum operations simultaneously and improve parallelization in circuit execution.
Additionally, Quantinuum researchers, in partnership with collaborators, achieved a significant milestone by demonstrating the first fault-tolerant technique using three logically encoded qubits. This breakthrough, conducted on the Honeywell-powered H1 quantum computer, showcased the system's ability to perform complex mathematical operations with enhanced error resilience.
2. System Model H2
The System Model H2 is Quantinuum's latest quantum computer, designed with a racetrack architecture. It incorporates several key features, including All-to-all connectivity, Mid-circuit measurement, Conditional logic, and Qubit reuse.
#8 IonQ (USA)
Found in 2015, IonQ is a leading manufacturer of trapped-ion quantum computers.
IonQ employs a unique trapped-ion technology, where naturally occurring atomic ions are isolated in a vacuum chamber and manipulated using lasers. These ions are trapped in 3D space by electric fields, ensuring high stability and long coherence times, which are essential for achieving high-fidelity qubits.
IonQ's quantum systems are available on-premise, via IonQ's Quantum Cloud, and accessible through cloud services such as Amazon Braket, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud.
Key Quantum Computers from IonQ
All quantum computers are based on IonQ's trapped-ion technology architecture.
1. IonQ Harmony
Released: 2020
Qubits: 11 qubits (retired in 2024)
IonQ Harmony is IonQ's first commercially available quantum computer, available on the IonQ Quantum Cloud and all major public clouds.
2. IonQ Aria quantum computer
Released: 2022
Qubits: 25 qubits
IonQ Aria is a powerful and versatile quantum computer, featuring a 25-qubit dynamically reconfigurable system. As the flagship model of IonQ's trapped-ion quantum computers, it is available on the IonQ Quantum Cloud and select public cloud platforms.
3. IonQ Forte Quantum Computer
Released: 2023
Qubits: 36 qubits
IonQ Forte is the latest cutting-edge quantum computer, featuring IonQ's largest single-core quantum processor and delivering the highest performance of any system to date. It is available through all major cloud providers.
The core innovation of Forte lies in the integration of acousto-optic deflector (AOD) technology. This groundbreaking advancement allows IonQ to dynamically control the direction of laser beams, precisely guiding quantum gates toward individual ions with high accuracy.
4. IonQ Tempo Quantum Computer
IonQ plans to release the Tempo quantum computer in 2025. The Tempo will have 64 qubits and will use barium instead of ytterbium.
#9 D-Wave Systems (Canada)
Founded in 1999, D-Wave specializes in quantum annealing technology, developing a series of adiabatic quantum annealing processors designed to tackle quadratic unconstrained binary optimization (QUBO) problems.
In 2011, D-Wave became the first quantum computing company to sell a commercial quantum computer, launching the D-Wave One, which was sold to Lockheed Martin.
D-Wave's quantum systems leverage the power of quantum annealing, designed to tackle optimization problems like identifying the most efficient solutions for complex datasets. These optimization challenges are common across industries such as logistics, finance, and machine learning.
In April 2024, D-Wave introduced a fast-anneal feature that enhances the performance of their quantum annealing systems.
In January 2025, D-Wave announced the Leap Quantum LaunchPad program, offering qualified participants a three-month free trial to access D-Wave's annealing quantum computing technology and support resources.
Key Quantum Computers from D-Wave
1. D-Wave One
Introduced in 2011, the D-Wave One was the first commercially available quantum computer. It featured a 128-qubit processor and utilized quantum annealing to solve optimization problems. This system marked a milestone in making quantum computing accessible for practical applications
2. D-Wave 2X
Released in 2015, the D-Wave 2X was the second commercially available quantum computer from D-Wave. It built upon the advancements of its predecessor, offering improved performance and reliability for complex computational tasks.
3. D-Wave 2000Q
Announced in 2017, the D-Wave 2000Q features 2,000 qubits.
4. The Advantage Quantum Computer
The Advantage system is the world's largest annealing quantum computer, boasting more than 5,000 qubits and 15-way connectivity. This configuration enables it to address computationally complex problems.
The Advantage system is specifically designed for business and research, offering enhanced performance for optimization and simulation tasks available on-premises or accessible through the D-Wave Leap™ quantum cloud service.
#10 Xanadu (Canada)
Xanadu Quantum Technologies is pioneering the use of photonics to build quantum computers. By utilizing light instead of electrons to represent qubits, Xanadu aims to enhance the scalability and efficiency of quantum systems.
Xanadu's Quantum Cloud platform offers direct access to photonic quantum computers, enabling users to seamlessly execute quantum algorithms. Through this platform or Amazon Braket, users can explore Borealis, Xanadu's flagship photonic quantum processor.
To support broader quantum computing development, Xanadu created PennyLane, a versatile open-source software library that allows anyone to run quantum commands on publicly accessible cloud-based quantum systems, such as IBM Q Experience and the University of Bristol's Quantum in the Cloud.
Key Quantum Computers from Xanadu
1. Borealis
Borealis is a programmable photonic quantum computer with 216 squeezed-state qubits, utilizing advanced photonics and quantum light sources to produce squeezed-light pulses.
As the first publicly cloud-deployed quantum computer, Borealis is available to users worldwide through Xanadu Cloud and Amazon Braket. It is particularly well-suited for solving Gaussian boson sampling problems—tasks that would take classical computers thousands of years to complete.
2. Aurora
Aurora, the world's first universal photonic quantum computer, features four modular server racks that are independently operated and connected through photonic networking. This 12-qubit system integrates 35 photonic chips and utilizes 13 kilometers of fiber optics, all functioning seamlessly at room temperature.
#11 Quantum Circuits(USA)
Quantum Circuits, Inc. specializes in developing superconducting quantum computers with a modular architecture, designed for scalability and high-speed algorithm execution. Their quantum processors are specifically engineered to address complex optimization and machine learning challenges while seamlessly integrating into existing infrastructure.
Key Quantum Computers from Quantum Circuits
On November 19, 2024, Quantum Circuits, Inc. unveiled its latest quantum hardware innovation, the Aqumen Seeker, the industry's first 8-qubit quantum processor utilizing dual-rail cavity qubits.
This groundbreaking system features built-in error detection, correcting errors before scaling up. Following Quantum Circuits' pragmatic approach of "correct first, then scale," Aqumen Seeker leverages Dual-Rail Cavity Qubits with advanced real-time control flow capabilities.
This design allows researchers and developers to achieve greater computational scale with fewer qubits, avoiding the need for brute-force methods.
#12 PsiQuantum (USA)
PsiQuantum is advancing quantum computing by leveraging photonic technology, using light to process quantum information.
While the company has not yet built a fully operational, commercially available quantum computer, they are currently developing and testing "intermediate systems," including chips, cabinets, and superconducting photon detectors. Instead of smaller prototypes, PsiQuantum is concentrating on building a large-scale quantum computer with one million qubits. Their goal is to have a functional, fault-tolerant, error-corrected quantum computer by late 2027.
#13 Infleqtion (USA)
Infleqtion, previously known as ColdQuanta, leverages cold-atom quantum technology to develop quantum computing and sensing systems. This technology involves using lasers to cool atoms to near absolute zero, effectively halting their motion. These ultra-cold atoms can then be manipulated into quantum matter, which underpins applications ranging from atomic clocks and quantum sensors to complex quantum computing systems.
In December 2022, the company rebranded as Infleqtion to highlight its focus on commercial quantum technologies. Their offerings include quantum lab equipment, quantum radio frequency receivers, positioning systems, and quantum components like vacuum systems and cryogenic processors that enhance system stability.
Infleqtion's cold-atom technology supports secure communication, cryptography, and quantum sensing. Winning the Q-Calc project boosted their expertise in quantum contextual AI, defense-related quantum AI applications, and data analytics. Their innovations span quantum simulation, information processing, atomic clocks, inertial sensing, and cold atom experimentation.
Key Quantum Computers from Infleqtion
Infleqtion has quantum computers, including neutral atom quantum computers and trapped atom vacuum systems.
1. Neutral atom quantum computers
Infleqtion's first quantum computer leverages neutral atoms and features long-range qubit connectivity, enabling advanced quantum error correction techniques.
2. Trapped atom vacuum systems
The miniMOT V2 is a compact, ready-made trapped atom vacuum system that enables researchers to effortlessly generate and manipulate quantum matter using rubidium (Rb) or cesium (Cs) atoms. Featuring an intuitive interface, the miniMOT V2 offers precise control over critical system parameters, thereby enhancing adaptability of cold atom experiments.
3. Hilbert Processor: Cloud-based quantum computer
Hilbert, Infleqtion's cloud-based, gate-driven quantum computer, uses the inherent scalability of neutral atoms to deliver robust connectivity, high fidelity, and long qubit lifetimes—all at room temperature, eliminating the need for refrigeration.
#14 Quantum Computing Inc
Quantum Computing Inc. (QCi) is an innovative leader in integrated photonics and quantum optics, delivering accessible quantum machines worldwide. Its nanophotonic-based quantum technology offers speed, accuracy, and security while operating at room temperature with low power requirements and minimal environmental constraints.
QCi's core nanophotonic-based technology supports a wide range of applications, from quantum computing to quantum sensing and imaging. Their product portfolio includes advanced solutions for high-performance computing, artificial intelligence, cybersecurity, and remote sensing.
Entropy Quantum Computer (EQC) from Quantum Computing Inc
Quantum Computing Inc. (QCi) developed the Dirac-3 Entropy Quantum Computer, specifically designed for optimization applications. The EQC uses fundamental quantum physics within a quantum photonic hardware system to produce useful qubits for complex computations.
The Dirac series offers powerful entropy computing capabilities, handling both binary and integer-based optimization problems. It supports over 11,000 qubits for binary tasks and more than 1,000 (n=64) qubits for integer-based problems—the highest variables and problem sizes currently available in quantum computing.
#15 ALICE & BOB (France)
Alice & Bob, a French quantum computing firm, specializes in self-correcting superconducting cat qubits, the first qubits with built-in error correction. This innovation paves a simpler path to fault-tolerant, universal gate-based quantum computing.
In March 2022, the company achieved a significant breakthrough in error correction, specifically addressing bit-flip challenges. Their cat-qubit stabilization approach extended resilience against bit-flip errors from just a few milliseconds to an impressive 2 minutes, showcasing remarkable progress.
In January 2025, Alice & Bob secured €100 million in funding to further develop this technology, aiming to build a useful quantum computer by 2030. The company's objective is to create one logical qubit within the next two years and to scale up to 100 logical qubits by 2028, utilizing approximately 1,500 cat qubits.
Key Quantum Chips from ALICE & BOB
Alice & Bob has not yet built a fully functional quantum computer. Currently, the company operates four quantum computers in their Paris lab, each containing between one and 16 cat qubits. While a logical qubit—crucial for practical quantum computing—has not yet been achieved, Alice & Bob continues to make strides in quantum chip development.
1. Boson: The first cat qubit chip, achieved in 2024.
2. Helium: The chip series aim at creating the company's first error-corrected logical qubit.
3. Lithium: The chip series designed to scale multi-logical-qubit systems.
4. Beryllium: The chip series focused on enabling a universal set of logical gates.
5. Graphene: The chip series expected to deliver a quantum computer for industrial use cases by 2030.
#16 QuEra Computing (USA)
QuEra Computing specializes in developing neutral-atom quantum computers with a focus on scalability and real-world applications. The company harnesses innovative neutral-atom research—originally pioneered at Harvard University and MIT—to offer a highly scalable and programmable quantum computing solution.
Key Quantum Computers from QuEra Computing
Aquila
Launched in November 2022, Aquila is QuEra Computing's debut quantum machine—a 256-qubit analog quantum computer built on neutral-atom technology.
It is the first and only neutral-atom quantum computer accessible to the public through Amazon Braket. Operating in analog processing mode, Aquila performs computations through continuous transformations of its internal quantum state, utilizing programmable arrays of neutral rubidium atoms trapped in a vacuum by focused laser beams.
#17 Amazon Web Services (USA)
Amazon Web Services' most well-known quantum computing service is Amazon Braket, a cloud-based platform that provides developers access to quantum computers and tools from the third-party quantum computing companies. These include D-Wave (quantum annealers), IonQ (ion-trap processors), Oxford Quantum Circuits, QuEra, Xanadu (photonic quantum computers), and Amazon's own Braket Quantum Simulator.
This cloud quantum computing service allows users to experiment with different quantum hardware architectures to find the best fit for their specific needs, all through a pay-as-you-go model.
In addition to hosting external quantum computers, AWS has been advancing its own quantum computing research. Amazon Web Services is a more recent player joining the race to build a quantum computer. But so far it has not yet developed its own fully operational quantum computer.
Ocelot Chip from Amazon Web Services
In February 2025, AWS unveiled its first quantum computing chip, named Ocelot. This prototype chip uses scalable architecture to reduce quantum error correction by up to 90%.
Ocelot is a prototype chip developed to test error correction techniques. It features a novel architecture, integrating cat qubit technology with quantum error correction components from the ground up. This marks the first time AWS researchers have combined these technologies into a scalable microchip, utilizing manufacturing processes adapted from the microelectronics industry.
#18 NVIDIA (USA)
Founded in 1993, NVIDIA has become a leading technology company, specializing in advanced computing hardware, software development, and cutting-edge artificial intelligence solutions.
During Nvidia's CES 2025 keynote and subsequent Wall Street analyst Q&A, CEO Jensen Huang provided a guarded stance on the timeline for practical quantum computing. He estimated that "very useful" practical commercially quantum computers are likely 15 to 30 years away, suggesting that useful quantum computing is probably about two decades away.
Key Quantum Computer from NVIDIA
In March 2023, NVIDIA introduced the DGX Quantum, the world's first GPU-accelerated quantum computing system. It combines the NVIDIA Grace Hopper Superchip with Quantum Machines' OPX quantum control platform, seamlessly integrating classical and quantum computing.
The system delivers ultra-low latency, efficiently handles large-scale AI and HPC workloads, and offers up to tenfold performance gains for quantum-classical research applications, supporting tasks such as calibration, control, and quantum error correction.
Featured Content




.png)
